The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Cybersecurity
In the fast-paced digital world of today, where commerce, communication, and human emotions are closely intertwined through technology, it is essential to safeguard this virtual space. Cybersecurity plays a crucial role in protecting against modern digital threats. This guide aims to provide you with the knowledge needed to understand, strengthen, and protect your digital assets from cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity is more than safeguarding digital assets; it's about protecting our way of life. While traditional defenses are important, they struggle to keep up with evolving threats. Thus, mastering cybersecurity is vital for individuals and organizations to defend against unauthorized access, breaches, and cyberattacks.
This ultimate guide to mastering cybersecurity is designed to serve as a comprehensive resource for understanding the vast landscape of digital security. From fundamental concepts to advanced protective strategies, the guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to fortify your digital defenses. Whether you're a beginner curious about password security or a professional looking to enhance your organization's defense mechanisms, this guide provides insights into the best practices, emerging trends, and pivotal technologies shaping the future of cybersecurity.
What is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity encompasses a set of practices, technologies, and processes that aim to safeguard networks, computers, programs, data, and information from unauthorized access, damage, or attack. It acts as a protective shield that defends against cyber threats that exploit vulnerabilities in the digital ecosystem. This discipline is critical in several areas, including information security, network security, operational security, data loss prevention, and physical security. Its importance cannot be overstated in today's era, where digital data is a valuable asset for both individuals and corporations.
The concept of cybersecurity extends beyond mere defense against external cyber threats. It also encompasses risk management and the ability to recover from breaches effectively as well as insider threats. With the digital landscape being an integral part of everyday life, the potential impact of cyber threats ranges from minor inconvenience to catastrophic financial and reputational damage. Cybersecurity practices are thus continually evolving to counteract these threats, involving not just technological solutions but also human vigilance and regulatory compliance.
Related Article: Common Cybersecurity Terms
Understanding Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are any potential malicious attack that seeks to unlawfully access data, disrupt digital operations, or damage information. These threats come in various forms, including viruses, worms, trojan horses, phishing attacks, spyware, and ransomware, each designed with specific mechanisms to exploit vulnerabilities within systems. The most concerning aspect of these threats is their evolution; as cybersecurity measures become more sophisticated, so too do the tactics of cybercriminals. Take for example Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). These are sophisticated cyberattacks carried out by skilled attackers, often state-affiliated, who target specific organizations to steal sensitive data over a long period of time. This necessitates constant vigilance, ongoing education, and the adaptation of cybersecurity strategies to mitigate the risks posed by these evolving threats.
Fundamentals of Cyber Security
Cybersecurity operates on fundamental principles and concepts that lay the groundwork for secure digital operations.
The Pillars of Protection
The pillars of cybersecurity form the foundational framework that supports the entirety of a robust digital security strategy, crucial for protecting against an array of cyber threats. These pillars include confidentiality, integrity, and availability, often abbreviated as the CIA Triad. Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is accessed only by authorized individuals, safeguarding personal and corporate data from unauthorized access or disclosure. Integrity focuses on the accuracy and consistency of data, protecting it from tampering or unauthorized changes, thus maintaining its trustworthiness. Lastly, Availability guarantees that information and resources are accessible to authorized users when needed, ensuring that services can continue without interruption even in the face of cyberattacks. Together, these pillars guide the development and implementation of comprehensive security measures, shaping the strategies that organizations and individuals employ to defend their digital assets and maintain the reliability and safety of their cyber environment.
Cyber Security Best Practices
Adhering to cybersecurity best practices is pivotal for enhancing your digital defense mechanisms. A key practice includes regularly updating software and security systems to combat potential vulnerabilities; these updates often contain patches for security loopholes that could be exploited by cybercriminals. Implementing strong, unique passwords across different platforms, and utilizing multifactor authentication adds an extra layer of protection, making unauthorized access considerably more challenging. These practices prevent password reuse attacks and password spray attacks, which attempt one password on many different accounts.
Equally crucial is educating oneself and team members about the dangers of phishing emails and how to recognize them, as human error remains one of the most common security vulnerabilities. Establishing secure, encrypted connections through VPNs, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks, further safeguards data from interception. Lastly, regular backups of critical data are essential to ensure recovery in the event of a data breach or ransomware attack. These practices, when consistently applied, form a strong foundation for a secure cyber environment.
Cyber Security Technologies
Cybersecurity technologies are essential tools to safeguard digital information and infrastructure from cyber threats. These tools range from basic antivirus software for malware detection to complex systems like firewalls controlling network traffic. Encryption protects data confidentiality, while Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Prevention Systems (IPS) identify and halt potential threats, respectively. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems offer a comprehensive security view by collecting and analyzing real-time data. Additionally, Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) are similar to SIEM but have automated responses to events. Advanced cybersecurity tech is crucial for proactive defense against evolving cyber threats.
Cyber Security Laws and Compliance
Overview Of Major Cybersecurity Laws And Regulations
As more information is shared online and our dependency on digital processes grows, so does the need to protect sensitive information. Numerous cybersecurity laws and regulations exist to safeguard data across different industries within the United States. Let's look at some of the most prominent regulations governing data security:
Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA 2002): Standing as the cornerstone of federal data security, FISMA mandates robust measures for protecting government information and systems. This act applies to all federal agencies, requiring them to implement comprehensive security controls, conduct regular risk assessments, and report security incidents promptly. By ensuring the integrity of government data, FISMA plays a crucial role in safeguarding national security and public trust.
Who does FISMA apply to?
- Federal agencies
- Contractors and vendors working with federal agencies
- State and local government agencies (while not directly bound to FISMA itself, many states and local governments have adopted similar regulations)
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): Within the financial sector, where sensitive information flows freely, GLBA establishes essential safeguards. This act requires financial institutions to protect customer data through a variety of measures, including encryption, access controls, and incident response plans. By enforcing these regulations, GLBA fosters trust within the financial sector and protects individuals' sensitive financial information.
Who does GLBA apply to?
- Banks and credit unions
- Securities firms
- Insurance companies
- Financial institutions’ subsidiaries
- Non-bank lenders (ie mortgage companies, payday lenders)
- Credit reporting agencies
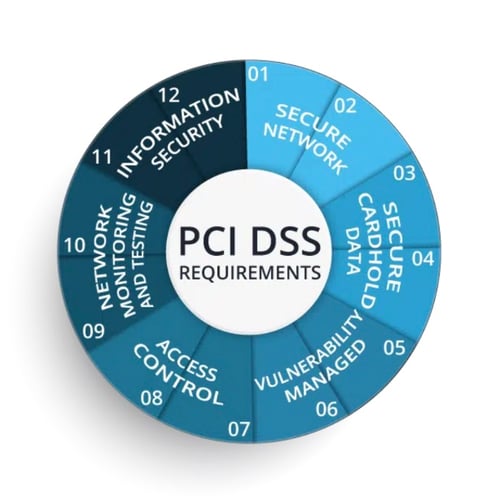
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Protecting consumers' financial information is crucial, and PCI DSS plays a vital role. This industry-wide standard mandates specific security controls for organizations that handle cardholder data, reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches. By enforcing these essential security measures, PCI DSS safeguards the financial transactions of millions of individuals worldwide. It should be noted that this is not a federal law and is a voluntary industry standard. However come companies like Visa and MasterCard won’t allow you to process their cards at your businesses if you don’t meet these standards. Some U.S. states have incorporated its principles or referenced it directly in their own laws related to data security and credit card protection.
1 Source: ITSupportGuys.com
Who does PCI DSS apply to?
- Retail stores
- Restaurants and hospitality businesses
- E-commerce businesses
- Payment processors
- Payment gateways
- Data centers
- Financial institutions
- Government agencies
Compliance Levels
1. Level 1 - Applies to: Merchants processing over 6 million card transactions annually.
Requirements: Most stringent, encompassing all 12 PCI DSS requirements, annual onsite report by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) or Internal Security Assessor (ISA), and additional merchant-specific requirements.
2. Level 2 - Applies to: Merchants processing 1 million to 6 million card transactions annually.
Requirements: All 12 PCI DSS requirements, annual self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ) completion, and potential for additional requirements based on the specific SAQ used.
3. Level 3 - Applies to: Merchants processing 20,000 to 1 million card transactions annually.
Requirements: All 12 PCI DSS requirements, annual SAQ completion, and potential for on-site assessments depending on the specific SAQ used.
4. Level 4 - Applies to: Merchants processing fewer than 20,000 card transactions annually.
Requirements: All 12 PCI DSS requirements and annual SAQ completion.
Choosing the Correct Level: For most merchants, determining the appropriate PCI DSS level is straightforward based on their transaction volume. However, it's crucial to consult the official PCI DSS website or a qualified professional to ensure accurate categorization and compliance fulfillment.
Learn more about PCI DSS
These key cybersecurity regulations represent just a glimpse into the complex world of data protection. Understanding and complying with these laws is essential for businesses of all sizes and industries. By prioritizing data security, we can collectively build a more secure and trustworthy digital future.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): In the healthcare industry, where patient privacy is paramount, HIPAA sets the gold standard for data protection. This act safeguards the privacy of protected health information (PHI) by outlining strict regulations on its use, disclosure, and security. By ensuring the confidentiality of patient data, HIPAA empowers individuals and fosters trust within the healthcare system.
Who does this apply to?
- Healthcare providers
- Health insurance companies, Medicare, Medicaid, and health plans
- Healthcare clearinghouses
- Business associates of the covered entities
- Government agencies (ie Department of Health, Social Security Administration)
“Roughly 75% of surveyed healthcare services stated their cybersecurity infrastructure is largely unprepared for cyber threats and confirmed their patient privacy and health data could be at risk.”
Source: HealthcareITnews.com
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA): Taking a pioneering approach to data privacy, California enacted CCPA and CPRA, granting residents significant control over their personal information. These groundbreaking laws require businesses to disclose what data they collect, offer opt-out options, and enable data deletion upon request. CCPA and CPRA set a precedent for data privacy rights, influencing regulations across the United States and beyond.
Who does this apply to?
- Businesses with gross annual revenue over $25 million (this includes revenue from all sources, not just California)
- Businesses that buy or sell the personal information of 50,000 or more California residents.
- Businesses that derive 50% or more of their annual revenue from selling California residents’ personal information
* Even if a business is not headquartered in California, it is still subject to CCPA/CPRA if it collects personal information from California residents
Who does this NOT apply to?
- Non-profit organizations
- Government agencies
- Businesses solely collecting employee data
Learn more about CCPA / Learn more about CPRA
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC): With national security at stake, the US Department of Defense established CMMC to ensure the cybersecurity preparedness of defense contractors. This certification program requires contractors to implement specific security measures based on maturity levels, safeguarding sensitive government information and critical infrastructure. By enforcing rigorous standards, CMMC strengthens the cybersecurity posture of the defense sector.
Who does CMMC apply to?
- Prime contractors (work directly with the Department of Defense (DoD)
- Subcontractors (provide goods and services to prime contractors)
- Subcontractors of any tier (regardless of where you are on the supply chain, if your work contributes to a DoD contract, CMMC applies to you)
- Non-US companies (foreign companies supporting US warfighters)
Learn more about CMMC
“25% of organizations spend less than 1,000 hours on compliance a year.”
Source: Drata.com
Compliance And Its Importance For Business
In our interconnected world, deciphering regulations and standards can feel like navigating a labyrinth. This is where compliance becomes a critical pillar for business success. But why exactly is compliance so important?
Firstly, compliance safeguards your business from legal and financial repercussions. Breaching regulations can result in hefty fines, penalties, and even lawsuits. This can not only damage your reputation but also cripple your financial stability, potentially jeopardizing the entire operation. By proactively adhering to relevant regulations, you minimize these risks and ensure your business operates within the legal framework.
Secondly, compliance fosters trust and transparency. Consumers and stakeholders increasingly value businesses that operate ethically and responsibly. Demonstrating your commitment to compliance through clear policies and procedures builds trust and transparency, attracting customers and partners who appreciate your commitment to doing the right thing. This translates to increased brand loyalty and stronger partnerships, contributing to long-term success.
Furthermore, compliance can enhance efficiency and innovation. By following standardized procedures and best practices, you streamline operations, minimize errors, and optimize resource allocation. This can significantly improve efficiency and free up resources for innovation and growth. Additionally, some regulations mandate specific data security measures, which ultimately enhance your cybersecurity posture and protect your valuable data.
Finally, compliance plays a role in creating a positive work environment. Adhering to labor regulations and ethical business practices fosters a positive and respectful workplace culture.
This translates to higher employee morale, engagement, and productivity, ultimately leading to a stronger and more resilient workforce.
In conclusion, compliance is not just a box-ticking exercise; it's a strategic investment in your business's future. By proactively embracing compliance, you mitigate risks, build trust, enhance efficiency, and cultivate a positive work environment, all crucial elements for sustainable growth and success in today's competitive market. Remember, compliance is not a destination but a continuous journey, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation. By making it an integral part of your business strategy, you pave the way for a brighter and more secure future.
International Organization for Standardization / International Electrotechnical Commission (ISO/IEC)
Securing our digital assets is paramount in today’s interconnected online environment. Organizations of all sizes and sectors face a constant barrage of cyber threats, making robust cybersecurity measures essential. To combat these threats, various international standards and frameworks have emerged, offering a structured approach to information security management.
This section delves into the world of these frameworks, exploring prominent examples like ISO/IEC 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). We'll explore their key features, benefits, and how they can empower your organization to navigate the cybersecurity landscape.
International Information Security Standards (IOS/IEC 27001)
This widely recognized framework provides a comprehensive roadmap for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). By focusing on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets, ISO/IEC 27001 helps organizations systematically manage and mitigate security risks. The standard doesn't dictate specific technologies but rather outlines a framework of best practices, allowing organizations to tailor their approach to their specific needs. Implementing and potentially seeking certification for ISO/IEC 27001 demonstrates an organization's commitment to information security, enhances internal control frameworks, and offers a competitive edge in today's data-driven world.
Learn more about IOS/IEC 27001
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
This framework was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. and takes a different approach compared to ISO/IEC 27001. Instead of a prescriptive set of requirements, the CSF acts as a voluntary, high-level framework that empowers organizations to manage their cybersecurity risks effectively. It outlines five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover, further divided into subcategories with informative references. This flexibility allows organizations of all sizes and industries to adapt the framework to their specific needs and risk profiles. Unlike ISO/IEC 27001, the CSF isn't directly certifiable, but organizations can demonstrate alignment and use it as a valuable reference point for strengthening their internal controls and building a robust cybersecurity posture.
Learn more about NIST Cybersecurity Framework
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
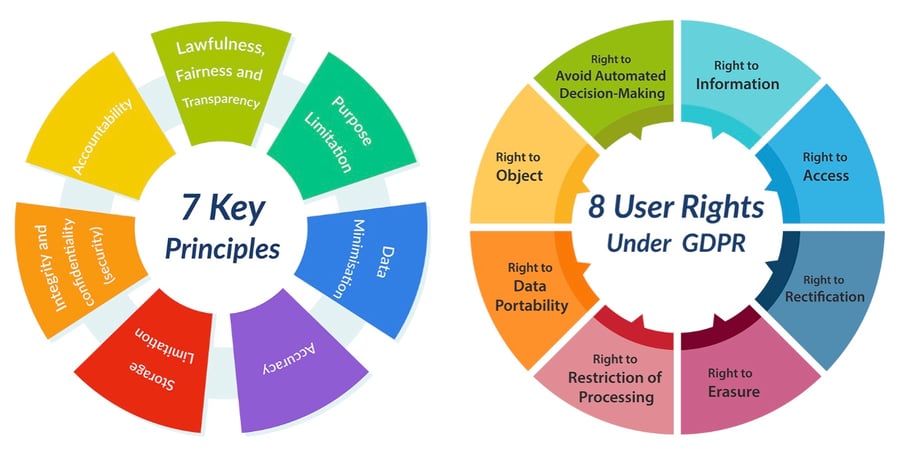
Implemented by the European Union, GDPR transcends the realm of purely technical cybersecurity standards. It focuses on protecting the fundamental right to privacy by regulating the collection, use, and protection of personal data within the EU and beyond. Unlike the frameworks mentioned earlier, the GDPR imposes legal obligations on organizations processing the personal data of EU residents, regardless of their location. It grants individuals various rights concerning their data, including the right to access, rectification, erasure, and restriction of processing. Organizations must adhere to strict principles like transparency, accountability, and data minimization to comply with the GDPR. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage. While not strictly a "cybersecurity" standard, the GDPR plays a crucial role in today's data-driven world, requiring careful consideration for organizations handling personal data of EU citizens.
2 Source: qrcsolutionz.com
How Do International Regulations Affect U.S. Companies?
While not directly mandatory in the United States, ISO/IEC 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and GDPR can still significantly impact companies operating within the country in several ways:
1. Market Competitiveness
Implementing these frameworks demonstrates a commitment to strong security practices and data protection, which can be a competitive advantage in the global marketplace. Many organizations, even those outside the EU, are increasingly requiring their vendors and partners to comply with these frameworks or demonstrate alignment with their principles.
2. Building Trust
Demonstrating adherence to recognized cybersecurity standards and data protection regulations like GDPR builds trust with customers and partners, particularly those with international operations or dealing with sensitive data. This can be crucial for acquiring and retaining business, especially in today's data-centric world.
3. Risk Management and Compliance
While not mandatory in the U.S., these frameworks can serve as valuable guides for managing cybersecurity risks and developing effective internal controls. By implementing these frameworks or aligning with their principles, companies can mitigate potential risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and non-compliance with emerging regulations.
4. Specific Industry Regulations
Some U.S. industries might have specific regulations that reference or require compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 or similar security standards. For instance, the healthcare industry may require HIPAA compliance, which overlaps with some aspects of data security addressed by ISO/IEC 27001.
5. GDPR's Impact on U.S. Companies
While not directly applicable to all U.S. companies, the GDPR can still have an impact if the company deals with the personal data of EU citizens. Companies need to be aware of the GDPR's requirements and take appropriate measures to comply if they collect, process, or store such data.
Therefore, even though not mandatory by law in the U.S., these frameworks and regulations offer valuable tools for U.S. companies to enhance their cybersecurity posture, build trust with stakeholders, and manage risks associated with data and information security.
Protecting Personal Data
Protecting personal data is paramount in today’s digital age, where identity theft, financial fraud, and privacy breaches are increasingly common. Personal information, from social security numbers to bank account details, is a valuable commodity for cybercriminals. When this data falls into the wrong hands, it can lead to devastating consequences for individuals, ranging from financial loss to long-term reputational damage. Furthermore, the emotional and psychological impact of personal data breaches can be profound, leading to a sense of vulnerability and mistrust in digital systems. Thus, safeguarding personal data is not just about preventing financial loss, but also about preserving personal integrity and trust in the increasingly interconnected world of digital interactions.
Future of Cyber Security
Stepping into the future of cybersecurity, we embark on a journey of rapid advancements and growing threats. With 2023 as a milestone year for integrating IoT devices and cloud tech, the anticipation for 2024 is to push boundaries further. The rise of wearable tech, smart appliances, and various IoT devices has necessitated heightened cloud security measures. However, challenges arise with routine updates causing malfunctions, data loss, and security breaches. The goal for 2024 and beyond is clear - establish robust security protocols to counter escalating cyber threats. This entails technical strategies like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular software updates, alongside fostering a culture of security awareness.
As our society becomes more digitally reliant, the risk of international cyberattacks targeting businesses looms larger. To counter this, companies must invest in advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying and neutralizing cyber threats proactively. It is crucial for businesses to harness the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance their cybersecurity defenses.
Despite AI complicating the cybersecurity landscape, it also provides viable solutions. Leveraging AI for automated tasks enables businesses to allocate resources effectively toward enhancing cybersecurity measures.
In the end, cybersecurity is a dynamic and essential aspect of our digital lives. By arming ourselves with knowledge and adopting best practices, we can collectively contribute to a more secure cyber world for everyone.

